- Hardware & Software Requirements
- DNS Prerequisites
- Installing Axigen on Linux
- Installing Axigen on Linux (Axigen X2 & X3)
- Installing Axigen on Windows
- Deploying & Running Axigen in VMware & VirtualBox
- Deploying & Running Axigen in Docker
- Performing the Initial Configuration (Onboarding)
- Starting / Stopping / Restarting Axigen
- About Axigen's Architecture
- Services and Modules
- Supported OS / Platforms and Web Clients
Updated: December 5, 2022
The Axigen virtual appliance is available starting with Axigen X2 Update 2 (10.2.2).
Introduction
The Axigen virtual appliance allows customers to run an Axigen based mail service within a VMware or VirtualBox environment.
Image Structure
The image relies on an Ubuntu image on top of which Axigen is installed (from DEB) and basic configuration is performed.
The virtual machine is configured as follows:
-
CPU: 2 cores
-
RAM: 4 GB
-
HDD: 50 GB; for larger deployments, you can add additional disks or mount points.
-
LAN: one network interface
-
OS: Ubuntu 22.04
The disk structure obeys the DEB defined structure:
-
/opt/axigen— binaries and other files -
/var/opt/axigen— data files
The axi-admin user password is set by default to a standard value and will be displayed before each local login.
Considerations About the Axigen Virtual Appliance
Network Configuration
By default, the image uses DHCP for network configuration.
Time Zone
By default, the time zone is set to Europe / London.
To set your preferred time zone, use:
To find your_time_zone, you can issue the following system command:
For example, to restrict the list to the European time zones, you can use:
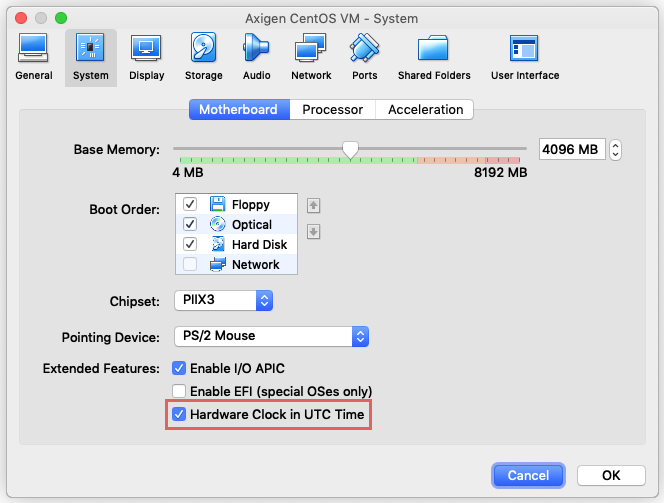
VirtualBox
When deploying in VirtualBox, it's mandatory to set HWCLOCK to UTC. More information here: https://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch03.html#settings-motherboard
Operating Axigen in a Virtual Appliance
Axigen does not have any particularities in operation comparing with a standard Linux install.
Examples:
-
Starting the Axigen service:
/etc/init.d/axigen start -
Stopping the Axigen service:
/etc/init.d/axigen stop -
Restarting the Axigen service:
/etc/init.d/axigen restart
Upgrading to newer versions is prone to the typical upgrade procedures.